Internet provider blocking IPTV has become an increasingly common issue affecting millions of cord-cutters worldwide. As traditional television viewership continues to decline and streaming services gain popularity, many Internet Service Providers (ISPs) have implemented various blocking mechanisms that prevent users from accessing IPTV content. This comprehensive guide explores the complex relationship between ISPs and IPTV services, providing you with the knowledge and tools needed to understand, detect, and overcome these restrictions.
The rise of IPTV technology has fundamentally changed how we consume television content, offering unprecedented flexibility and cost savings compared to traditional cable and satellite services. However, this technological advancement has created tension between ISPs, content creators, and consumers, leading to a cat-and-mouse game of blocking and circumvention techniques. Understanding why internet providers block IPTV services and how to effectively address these restrictions is crucial for anyone looking to maintain unrestricted access to their preferred streaming content.
Table of Contents
What Is IPTV and Why Do Internet Providers Block It?
Understanding IPTV Technology
Internet Protocol Television (IPTV) represents a revolutionary approach to delivering television content through internet protocols rather than traditional broadcast methods. Unlike conventional cable or satellite TV that relies on dedicated infrastructure and proprietary signals, IPTV leverages your existing internet connection to stream live television channels, on-demand content, and interactive services directly to your devices. This technology has democratized access to global content, allowing users to watch international channels, sports events, and premium programming at a fraction of traditional costs.
The fundamental difference between IPTV and traditional broadcasting lies in the delivery mechanism and user control. Traditional television broadcasts content to all subscribers simultaneously, regardless of whether they’re watching, while IPTV delivers content on-demand, streaming only what users actively request. This unicast delivery method significantly reduces bandwidth waste and allows for interactive features like pause, rewind, and time-shifting that have become standard expectations in modern entertainment consumption.
Legitimate IPTV services include well-known platforms such as:
- YouTube TV – Google’s comprehensive live TV streaming service
- Hulu + Live TV – Disney’s hybrid on-demand and live television platform
- Sling TV – Dish Network’s flexible streaming service
- FuboTV – Sports-focused streaming platform
- AT&T TV Now – AT&T’s internet-based television service
However, the IPTV landscape also includes numerous unauthorized services that redistribute copyrighted content without proper licensing agreements. These services often offer premium channels, pay-per-view events, and international content at significantly reduced prices, making them attractive to cost-conscious consumers but problematic for content creators and distributors.
Common Reasons ISPs IPTV Block Services
Internet providers block IPTV for several interconnected reasons that span technical, legal, and business considerations. Understanding these motivations helps explain why certain IPTV services face restrictions while others operate without interference. The primary driver behind ISP blocking is bandwidth management, as IPTV streaming can consume substantial network resources, particularly during peak usage hours when multiple subscribers simultaneously stream high-definition content.
Network congestion represents a significant challenge for ISPs, especially those operating older infrastructure or serving densely populated areas. A single 4K IPTV stream can consume 25-35 Mbps of bandwidth, and when hundreds or thousands of subscribers stream simultaneously, it can overwhelm network capacity and degrade service quality for all users. ISPs often implement traffic shaping or blocking measures to maintain overall network performance, prioritizing certain types of traffic over others.
Copyright infringement concerns constitute another major factor driving ISP IPTV blocking. Many unauthorized IPTV services distribute copyrighted content without proper licensing, exposing ISPs to potential legal liability under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and similar international legislation. Content creators and distributors regularly send takedown notices to ISPs, requesting the blocking of specific services or IP addresses associated with copyright violations.
Business partnerships between ISPs and traditional television providers create additional incentives for IPTV blocking. Many major ISPs also operate cable television services or maintain revenue-sharing agreements with content distributors. Allowing unrestricted access to competing IPTV services could cannibalize their traditional television revenue streams, creating conflicts of interest that influence blocking decisions.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) technology enables ISPs to analyze internet traffic in real-time, identifying IPTV streams based on packet signatures, protocols, and destination addresses. This sophisticated monitoring capability allows ISPs to selectively block or throttle IPTV traffic while maintaining normal speeds for other internet activities. The implementation of DPI has made ISP blocking more precise and harder to detect, as users may experience degraded IPTV performance without realizing their ISP is actively interfering with their connection.
How to Tell If Your Internet Provider Is Blocking IPTV
Signs Your ISP Is Blocking IPTV Streams
Identifying internet provider IPTV blocking requires careful observation of your streaming experience and systematic testing to distinguish between ISP interference and other potential causes of poor performance. The most common indicator of ISP blocking is inconsistent streaming quality that varies significantly between different types of content or services. If you experience smooth browsing, fast downloads, and excellent performance with mainstream streaming services like Netflix or YouTube, but encounter persistent problems with IPTV applications, this pattern suggests targeted blocking rather than general connectivity issues.
Buffering and connection timeouts represent the most frequent symptoms of ISP IPTV blocking. Unlike random buffering caused by temporary network congestion, ISP-induced buffering typically follows predictable patterns, occurring consistently with specific IPTV services or during particular time periods. Users often report that IPTV streams buffer excessively during peak evening hours (7-11 PM) when ISPs implement traffic management policies, while the same content streams smoothly during off-peak periods.
Complete inability to access IPTV applications or websites represents the most severe form of ISP blocking. This occurs when ISPs implement DNS filtering, IP address blacklisting, or port blocking that prevents any communication with IPTV servers. Users experiencing this level of blocking often find that IPTV applications fail to load channel lists, display connection errors, or crash immediately upon startup.
Geographic inconsistencies in IPTV performance can also indicate ISP blocking. If the same IPTV service works perfectly when accessed through mobile data, public WiFi, or different internet connections, but consistently fails on your home network, this strongly suggests ISP-level interference. Many users discover blocking by testing their IPTV service at friends’ houses or using mobile hotspots as alternative internet sources.
Testing Methods to Confirm IPTV Blocking
Systematic testing is essential for confirming whether your internet provider is blocking IPTV services and determining the specific blocking methods being employed. The most effective approach involves comparative analysis using multiple connection methods and monitoring tools to isolate ISP-specific issues from general connectivity problems.
VPN testing provides the most reliable method for confirming ISP IPTV blocking. By connecting to a reputable VPN service and testing your IPTV performance, you can determine whether routing traffic through encrypted tunnels resolves streaming issues. If IPTV services work perfectly through a VPN but fail on your direct connection, this definitively proves ISP interference. When conducting VPN tests, try multiple server locations and protocols to ensure consistent results.
Speed testing procedures should compare bandwidth performance across different types of traffic. Use standard speed test tools like Speedtest.net or Fast.com to measure your general internet performance, then compare these results with IPTV-specific speed tests during active streaming sessions. Significant discrepancies between general internet speeds and IPTV streaming performance indicate targeted throttling or blocking.
Port connectivity testing helps identify specific blocking methods used by your ISP. Many IPTV services use standard ports (8080, 8000, 554) that ISPs commonly block. Use network diagnostic tools like Telnet or online port checkers to test connectivity to IPTV server ports. If these ports are blocked while others remain accessible, it confirms port-based filtering.
DNS resolution testing can reveal DNS-based blocking techniques. Try changing your DNS servers to public alternatives like Google DNS (8.8.8.8, 8.8.4.4) or Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1, 1.0.0.1) and test IPTV performance. If changing DNS servers resolves connectivity issues, your ISP is likely using DNS filtering to block IPTV services.
ISP Throttling vs. Complete IPTV Blocking
Understanding the distinction between ISP throttling and complete IPTV blocking is crucial for selecting appropriate countermeasures and setting realistic expectations for potential solutions. Throttling represents a more subtle form of interference where ISPs reduce bandwidth allocation for IPTV traffic without completely preventing access, while complete blocking prevents any communication with IPTV services.
Bandwidth throttling symptoms include:
- Reduced video quality that doesn’t match your internet plan’s advertised speeds
- Consistent buffering during high-definition streams while standard definition works normally
- Gradual degradation of streaming quality over time during extended viewing sessions
- Performance that improves significantly during off-peak hours
Complete blocking indicators include:
- Total inability to connect to IPTV servers or applications
- DNS resolution failures for IPTV service domains
- Connection timeout errors when attempting to access IPTV content
- IPTV applications that fail to load channel guides or authentication systems
Time-based restrictions represent a hybrid approach where ISPs implement blocking or throttling during specific periods, typically peak usage hours when network congestion is highest. Users experiencing time-based restrictions often find that IPTV services work perfectly during early morning or late-night hours but become unusable during prime time viewing periods.
Which Internet Providers Block IPTV Services?
Major ISPs Known for IPTV Restrictions
The landscape of internet provider IPTV blocking varies significantly across different ISPs, with some implementing aggressive blocking measures while others maintain relatively open policies. Understanding which providers are most likely to interfere with IPTV services helps consumers make informed decisions when selecting internet service and prepares them for potential restrictions.
Comcast/Xfinity has gained notoriety for implementing some of the most sophisticated IPTV blocking measures in the industry. The company utilizes advanced Deep Packet Inspection technology to identify and throttle IPTV traffic, particularly targeting unauthorized streaming services. Comcast’s blocking efforts intensified following several high-profile copyright infringement lawsuits and pressure from content industry partners. Users frequently report that popular IPTV applications experience severe buffering or complete connectivity failures on Xfinity networks, while the same services work flawlessly on alternative ISPs.
Verizon FiOS employs a more selective approach to IPTV blocking, focusing primarily on services that compete directly with their own television offerings. The company’s fiber-optic infrastructure provides ample bandwidth for IPTV streaming, but business considerations often drive blocking decisions. Verizon has been particularly aggressive in blocking sports-focused IPTV services that offer NFL, NBA, and MLB content that competes with their premium television packages.
AT&T Internet services have implemented increasingly restrictive IPTV policies following the company’s acquisition of DirecTV and subsequent launch of AT&T TV Now. The integration of AT&T’s internet and television services has created strong incentives to block competing IPTV platforms. Users report that AT&T employs both DNS filtering and traffic shaping to degrade IPTV performance while maintaining optimal speeds for their own streaming services.
Spectrum/Charter Communications has adopted a regional approach to IPTV blocking, with policies varying significantly across different service areas. Markets with high competition from streaming services tend to experience more aggressive blocking, while rural areas with limited entertainment options often see more lenient policies. Spectrum’s blocking methods primarily focus on port filtering and bandwidth throttling rather than complete service blocking.
Cox Communications has implemented some of the most transparent IPTV blocking policies, explicitly stating in their terms of service that certain streaming activities may be restricted or throttled. The company’s approach focuses on network management during peak usage periods, with IPTV services experiencing reduced priority compared to web browsing, email, and other “essential” internet activities.
Regional and International ISP Blocking
International ISP IPTV blocking practices vary dramatically based on local regulations, market competition, and government policies. European ISPs face strict net neutrality regulations that limit their ability to block or throttle specific services, while ISPs in other regions operate with greater freedom to implement restrictive policies.
European ISP restrictions are generally more limited due to comprehensive net neutrality legislation, but several major providers have found creative ways to discourage IPTV usage. British Telecom (BT) and Virgin Media have implemented “fair usage” policies that throttle heavy streaming users during peak hours, effectively targeting IPTV subscribers without explicitly blocking services. German ISPs like Deutsche Telekom have focused on DNS filtering to block access to unauthorized IPTV services while maintaining access to legitimate platforms.
Canadian internet provider policies reflect the country’s strong telecommunications regulations and competitive market structure. Major providers like Rogers, Bell, and Shaw have generally avoided aggressive IPTV blocking due to regulatory oversight and competition from alternative ISPs. However, these providers have implemented sophisticated traffic management systems that prioritize their own television services over third-party IPTV platforms.
Australian ISP blocking practices have been heavily influenced by government-mandated website blocking orders targeting copyright infringement. Providers like Telstra, Optus, and TPG have implemented comprehensive blocking systems that affect both legitimate and unauthorized IPTV services. The Australian government’s site-blocking legislation has created a framework that ISPs use to justify broader IPTV restrictions.
Asian market restrictions vary widely based on local internet governance policies and market structures. Chinese ISPs operate under strict government oversight that limits access to international IPTV services, while ISPs in countries like South Korea and Japan focus primarily on bandwidth management rather than content blocking. Indian ISPs have implemented some of the most aggressive IPTV blocking measures globally, targeting both domestic and international streaming services.
ISP Blocking Methods and Technologies
Modern ISP IPTV blocking technologies have evolved far beyond simple IP address blacklists, incorporating sophisticated traffic analysis and real-time filtering systems that can identify and block IPTV streams with remarkable precision. Understanding these technologies helps users select appropriate countermeasures and explains why some blocking methods are more difficult to circumvent than others.
Deep Packet Inspection (DPI) represents the most advanced blocking technology currently deployed by major ISPs. DPI systems analyze the actual content of internet packets in real-time, identifying IPTV streams based on protocol signatures, packet timing patterns, and data structures. This technology can distinguish between different types of video streaming, allowing ISPs to block IPTV services while maintaining normal performance for platforms like YouTube or Netflix. DPI systems are particularly effective because they operate at the network level and can adapt to new IPTV protocols and services automatically.
DNS filtering and redirection provides ISPs with a cost-effective method for blocking access to IPTV services without requiring expensive DPI infrastructure. By controlling the DNS servers that translate domain names into IP addresses, ISPs can prevent users from connecting to IPTV services or redirect them to warning pages. DNS filtering is relatively easy to implement and maintain, making it popular among smaller ISPs with limited technical resources.
Port blocking techniques target the specific network ports commonly used by IPTV services. Many IPTV platforms use standard ports like 8080, 8000, or 554 for streaming content, and ISPs can block these ports to prevent IPTV access while maintaining normal internet functionality. Port blocking is less sophisticated than DPI but remains effective against many IPTV services that haven’t implemented port randomization or encryption.
IP address blacklisting involves maintaining databases of known IPTV server addresses and blocking all traffic to these destinations. While this method is relatively simple to implement, it requires constant maintenance as IPTV services frequently change server locations and IP addresses. Some ISPs use automated systems that monitor for new IPTV servers and add them to blacklists in real-time.
Traffic shaping methods allow ISPs to reduce bandwidth allocation for IPTV traffic without completely blocking access. These systems can identify IPTV streams and automatically reduce their priority during network congestion, causing buffering and quality degradation. Traffic shaping is often preferred by ISPs because it’s less likely to generate customer complaints while still discouraging IPTV usage.
Legal Implications of ISP IPTV Blocking
Net Neutrality and IPTV Access Rights
The intersection of net neutrality principles and ISP IPTV blocking creates a complex legal landscape that continues to evolve as regulators, ISPs, and consumer advocates debate the appropriate balance between network management and open internet access. Net neutrality regulations, where they exist, generally prohibit ISPs from blocking or throttling specific types of content, but enforcement varies significantly across different jurisdictions and regulatory frameworks.
Current net neutrality regulations in the United States have undergone significant changes in recent years, with rules being implemented, repealed, and reinstated based on changing political administrations. The 2021 restoration of net neutrality protections under the Biden administration theoretically prohibits ISPs from blocking or throttling IPTV services, but enforcement mechanisms remain limited and many ISPs continue implementing blocking measures under the guise of “reasonable network management.”
Consumer rights regarding internet access extend beyond simple connectivity to include expectations of equal treatment for all legal internet traffic. The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) has established principles stating that consumers should have access to the lawful internet content and applications of their choice, but the definition of “lawful” content remains contentious when applied to IPTV services that may operate in legal gray areas.
Legal challenges to ISP blocking have produced mixed results, with courts generally supporting ISP rights to manage their networks while also recognizing consumer expectations of open internet access. Several class-action lawsuits have been filed against major ISPs for IPTV blocking, but most have been settled out of court or dismissed based on terms of service agreements that give ISPs broad discretion over network management practices.
FCC guidelines and enforcement regarding IPTV blocking remain inconsistent and politically influenced. While the FCC has issued statements supporting net neutrality principles, actual enforcement actions against ISPs for IPTV blocking have been rare. The commission’s approach tends to focus on egregious cases of blocking rather than subtle throttling or traffic management practices that affect IPTV performance.
When ISP Blocking Is Legal vs. Illegal
Determining the legality of internet provider IPTV blocking requires careful analysis of multiple factors including the specific blocking methods used, the nature of the IPTV service being blocked, applicable regulations, and the ISP’s stated justifications for implementing restrictions. The legal landscape is further complicated by the fact that many IPTV services operate in regulatory gray areas, making it difficult to determine whether blocking such services violates consumer protection laws.
Court-ordered blocking scenarios represent the clearest cases where ISP IPTV blocking is legally justified and often mandatory. When content creators obtain court injunctions against specific IPTV services for copyright infringement, ISPs may be legally required to block access to these services. These court orders typically specify particular domain names, IP addresses, or services that must be blocked, providing ISPs with legal protection for their blocking activities.
Copyright protection measures implemented by ISPs often receive legal protection under the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (DMCA) and similar international legislation. ISPs can argue that blocking IPTV services helps them avoid liability for copyright infringement by their subscribers, particularly when these services are known to distribute unauthorized content. However, the legality of preemptive blocking based on assumptions about copyright infringement remains contested.
Terms of service violations provide ISPs with contractual justification for blocking IPTV services, even when such blocking might otherwise violate net neutrality principles. Most ISP service agreements include broad language prohibiting activities that consume “excessive” bandwidth or interfere with network performance, giving providers legal cover for IPTV blocking measures. However, courts have sometimes found such terms to be unconscionable or deceptive when applied too broadly.
Legitimate network management represents the most common legal justification for ISP IPTV blocking, but the definition of “legitimate” remains highly contested. ISPs argue that blocking or throttling IPTV traffic during peak usage periods is necessary to maintain overall network performance and prevent service degradation for other customers. Consumer advocates counter that such practices violate net neutrality principles and constitute unfair discrimination against specific types of content.
Proven Solutions to Bypass Internet Provider IPTV Blocking
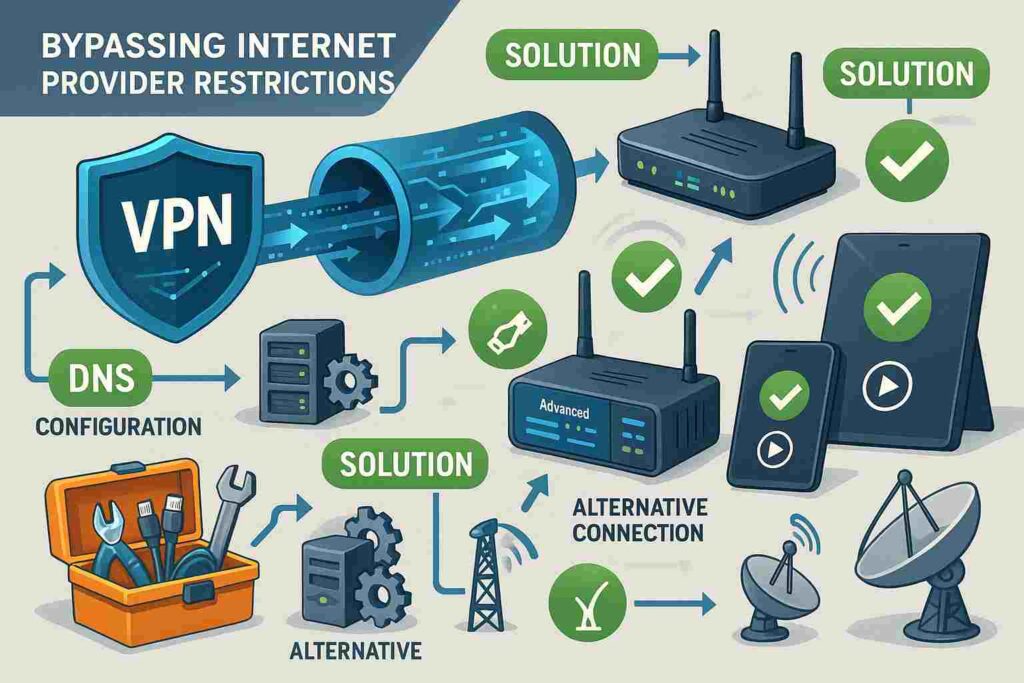
VPN Solutions for IPTV Unblocking
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) represent the most effective and widely-used solution for bypassing internet provider IPTV blocking, offering users the ability to encrypt their internet traffic and route it through servers located in different geographic regions. VPNs work by creating secure tunnels between your device and VPN servers, making it impossible for ISPs to analyze or block specific types of traffic while also masking your true IP address and location.
Best VPNs for IPTV streaming must balance several critical factors including connection speed, server reliability, encryption strength, and compatibility with streaming devices. ExpressVPN consistently ranks among the top choices for IPTV users due to its extensive server network spanning 94 countries, optimized streaming servers, and robust encryption protocols that effectively bypass ISP blocking measures. The service maintains consistently high speeds even when connected to distant servers, making it ideal for high-definition IPTV streaming.
NordVPN offers specialized features particularly valuable for IPTV users, including dedicated IP addresses that reduce the likelihood of being blocked by streaming services, double VPN encryption for enhanced security, and SmartPlay technology that automatically selects optimal servers for streaming content. The service’s CyberSec feature also blocks malicious websites and ads that commonly affect unauthorized IPTV services.
Surfshark provides exceptional value for households with multiple IPTV devices, offering unlimited simultaneous connections and specialized streaming servers optimized for video content. The service’s CleanWeb feature blocks ads and trackers that can interfere with IPTV performance, while its Camouflage Mode makes VPN traffic appear as regular internet browsing to ISPs using advanced detection methods.
VPN setup guides for different devices vary significantly based on the specific hardware and operating systems involved. For Android TV boxes, the most common IPTV devices, VPN installation typically involves downloading the provider’s Android app from the Google Play Store or sideloading APK files for devices without Play Store access. Most premium VPN services offer dedicated Android TV apps with simplified interfaces optimized for remote control navigation.
Smart TV VPN setup often requires more complex configuration since many smart TV platforms don’t support native VPN applications. Users typically need to configure VPN connections at the router level or use features like Smart DNS that route specific traffic through VPN servers without requiring full device encryption. Some VPN providers offer dedicated smart TV apps for platforms like Samsung Tizen or LG webOS, but compatibility varies significantly across different models and firmware versions.
Router-level VPN configuration provides the most comprehensive solution for protecting all IPTV devices in a household, but requires compatible router hardware and technical expertise. Users need routers that support VPN client functionality, either through manufacturer firmware or third-party alternatives like DD-WRT or OpenWrt. Once configured, router-level VPNs automatically protect all connected devices without requiring individual app installations or configurations.
DNS Configuration Changes
DNS (Domain Name System) configuration modifications represent one of the simplest and most cost-effective methods for bypassing certain types of ISP IPTV blocking, particularly when ISPs use DNS filtering to prevent access to IPTV services. By changing your DNS servers from ISP-provided defaults to public alternatives, you can often restore access to blocked IPTV services while maintaining normal internet performance for other activities.
Public DNS servers offer several advantages over ISP-provided DNS services, including improved privacy, faster response times, and resistance to censorship or blocking measures. Google DNS (8.8.8.8 and 8.8.4.4) provides reliable performance and extensive global infrastructure, making it an excellent choice for IPTV users experiencing DNS-based blocking. Google’s DNS servers are optimized for speed and rarely block legitimate services, though they may not bypass more sophisticated blocking methods.
Cloudflare DNS (1.1.1.1 and 1.0.0.1) emphasizes privacy and security, promising not to log user queries or sell data to third parties. Cloudflare’s DNS service often provides faster response times than Google DNS and includes built-in security features that protect against malicious websites and phishing attempts. The service’s commitment to privacy makes it particularly attractive for IPTV users concerned about ISP monitoring of their streaming activities.
OpenDNS (208.67.222.222 and 208.67.220.220) offers customizable filtering options and enhanced security features, though its filtering capabilities can sometimes interfere with IPTV access. The service provides detailed statistics about DNS queries and allows users to configure custom blocking rules, making it suitable for users who want more control over their DNS resolution.
Router DNS modification provides the most comprehensive solution for changing DNS settings across all devices in a household. Most modern routers allow users to specify custom DNS servers through their web-based administration interfaces, typically found in the WAN or Internet connection settings. Once configured at the router level, all connected devices automatically use the specified DNS servers without requiring individual device configuration.
Device-specific DNS setup may be necessary for devices that don’t respect router-level DNS settings or when users want different DNS configurations for specific devices. Android devices can be configured to use custom DNS servers through the WiFi settings menu, while iOS devices require DNS configuration through the WiFi network settings. Windows and Mac computers allow DNS configuration through network adapter settings, providing users with granular control over DNS resolution.
Proxy Servers and SOCKS5 Solutions
Proxy servers offer an alternative approach to bypassing ISP IPTV blocking by routing internet traffic through intermediate servers that mask the user’s true IP address and location. Unlike VPNs that encrypt all internet traffic, proxies typically handle specific applications or protocols, making them potentially faster for IPTV streaming while providing sufficient anonymity to bypass ISP restrictions.
SOCKS5 proxies represent the most advanced proxy protocol for IPTV applications, offering superior performance and compatibility compared to older HTTP proxies. SOCKS5 proxies can handle any type of internet traffic, including the UDP protocols commonly used by IPTV services, while providing authentication mechanisms that prevent unauthorized access. Many premium proxy services offer dedicated SOCKS5 servers optimized for streaming applications with minimal latency and maximum throughput.
SOCKS5 proxy configuration varies depending on the specific IPTV application and device being used. Most modern IPTV players include built-in proxy support that allows users to specify SOCKS5 server details including hostname, port number, username, and password. Popular IPTV applications like Kodi, VLC Media Player, and Perfect Player all support SOCKS5 proxy configuration through their network settings menus.
HTTP proxy alternatives may be suitable for IPTV services that use web-based streaming protocols, though they’re generally less compatible with traditional IPTV applications that rely on specialized streaming protocols. HTTP proxies are typically easier to configure and may offer better performance for web-based IPTV services, but they don’t provide the same level of protocol compatibility as SOCKS5 proxies.
Residential proxy benefits include IP addresses that appear to belong to regular internet users rather than commercial proxy services, making them less likely to be detected and blocked by ISPs or IPTV services. Residential proxies typically offer better compatibility with geo-restricted content and are less likely to trigger anti-proxy measures implemented by streaming services. However, residential proxies are generally more expensive than datacenter proxies and may offer lower performance due to their reliance on consumer internet connections.
Setup instructions for popular devices require careful attention to application-specific configuration requirements and network settings. Android TV boxes typically support proxy configuration through individual IPTV applications rather than system-wide settings, requiring users to configure proxy details separately for each streaming app. Smart TVs may require proxy configuration at the router level since many smart TV platforms don’t support application-level proxy settings.
Port and Protocol Modifications
Port and protocol modifications provide advanced users with sophisticated methods for bypassing ISP IPTV blocking that targets specific network ports or communication protocols commonly used by streaming services. These techniques require deeper technical knowledge but can be highly effective against ISPs that use port-based filtering or protocol analysis to identify and block IPTV traffic.
Changing default IPTV ports involves configuring IPTV services and applications to use non-standard port numbers that are less likely to be blocked by ISPs. Many IPTV services use common ports like 8080, 8000, or 554 that ISPs frequently target for blocking, but most services also support alternative ports that can be specified in application settings or M3U playlist files. Users can experiment with different port numbers to find combinations that work reliably with their ISP.
Protocol switching techniques allow users to change the underlying communication protocols used by IPTV services, potentially bypassing ISP blocking that targets specific protocol signatures. Many IPTV services support multiple protocols including HTTP, HTTPS, RTMP, and HLS, each with different characteristics that may be more or less likely to trigger ISP blocking measures. HTTPS protocols, in particular, provide encryption that makes it difficult for ISPs to analyze traffic content.
Router port forwarding can help optimize IPTV performance and bypass certain types of blocking by ensuring that incoming IPTV traffic is properly routed to the correct devices. Port forwarding rules specify that traffic arriving on specific ports should be directed to particular devices on the local network, potentially improving connection reliability and reducing buffering. However, port forwarding requires static IP addresses for IPTV devices and careful configuration to avoid security vulnerabilities.
Firewall configuration adjustments may be necessary to ensure that modified ports and protocols can communicate properly through network security systems. Users need to create firewall rules that allow IPTV traffic on non-standard ports while maintaining security for other network activities. Most modern routers include built-in firewalls that can be configured through web-based interfaces, though advanced configurations may require command-line access or third-party firmware.
Technical Workarounds for IPTV Blocking
Router-Level Solutions
Router-level solutions for bypassing internet provider IPTV blocking offer the most comprehensive and transparent approach to protecting all IPTV devices in a household, requiring minimal configuration on individual devices while providing consistent protection against ISP interference. These solutions typically involve modifying router firmware, configuring VPN connections, or implementing advanced networking features that mask IPTV traffic from ISP detection systems.
Firmware modifications using alternative router operating systems like DD-WRT, OpenWrt, or Tomato unlock advanced networking capabilities that aren’t available in manufacturer firmware. These open-source firmware alternatives provide extensive VPN client support, traffic shaping capabilities, and advanced firewall features that can effectively bypass ISP IPTV blocking. DD-WRT, in particular, offers built-in support for multiple VPN protocols and includes features like policy-based routing that can automatically route IPTV traffic through VPN connections while maintaining direct connections for other internet activities.
OpenWrt firmware provides the most flexibility for advanced users, offering a complete Linux-based operating system that can be customized with additional software packages and networking tools. OpenWrt supports advanced features like load balancing across multiple internet connections, traffic analysis tools for monitoring ISP blocking attempts, and mesh networking capabilities that can distribute IPTV traffic across multiple access points to avoid detection.
VPN router setup involves configuring routers to establish permanent VPN connections that automatically protect all connected devices without requiring individual VPN client installations. Most premium VPN services provide detailed setup guides for popular router models, including specific configuration files and step-by-step instructions. ASUS routers with Merlin firmware offer particularly user-friendly VPN client interfaces, while Netgear routers with DD-WRT provide extensive customization options for advanced users.
Mesh network configurations can help distribute IPTV traffic across multiple access points and internet connections, making it more difficult for ISPs to identify and block streaming activities. Modern mesh systems like ASUS AiMesh, Netgear Orbi, and Eero Pro support advanced features like band steering and load balancing that can optimize IPTV performance while reducing the likelihood of triggering ISP blocking measures.
Dual-WAN setups allow users to combine multiple internet connections for improved reliability and performance, while also providing backup connectivity if one ISP implements blocking measures. Dual-WAN configurations can automatically failover to secondary internet connections when primary connections experience problems, ensuring uninterrupted IPTV access even when ISPs implement temporary blocking measures. Advanced dual-WAN setups can also implement load balancing that distributes IPTV traffic across multiple ISPs to avoid triggering bandwidth-based blocking.
Device-Specific Bypass Methods
Device-specific bypass methods for IPTV blocking require tailored approaches based on the unique capabilities and limitations of different streaming hardware platforms. Each device category presents distinct opportunities and challenges for implementing effective blocking countermeasures, from simple configuration changes to advanced software modifications that unlock additional networking capabilities.
Android TV box configurations offer the most flexibility for implementing IPTV blocking bypasses due to the platform’s open architecture and extensive app ecosystem. Users can install VPN applications directly from the Google Play Store or sideload specialized networking apps that provide advanced proxy and tunneling capabilities. NVIDIA Shield TV devices, in particular, offer excellent performance for VPN-protected IPTV streaming due to their powerful processors and extensive memory, while budget Android boxes may require optimization to maintain acceptable performance when using encryption.
Kodi-based IPTV setups on Android devices can benefit from specialized add-ons that provide built-in proxy and VPN integration. The VPN Manager for OpenVPN add-on allows users to configure VPN connections directly within Kodi, automatically protecting IPTV streams without requiring separate VPN applications. Similarly, the Proxy Settings add-on enables SOCKS5 proxy configuration for individual IPTV sources, providing granular control over which streams are protected.
Smart TV workarounds typically require more creative approaches since most smart TV platforms don’t support native VPN or proxy applications. Samsung Tizen and LG webOS smart TVs can often benefit from Smart DNS services that route specific traffic through proxy servers without requiring full VPN encryption. Users can configure Smart DNS settings through the TV’s network configuration menu, though compatibility varies significantly across different models and firmware versions.
Apple TV IPTV configurations present unique challenges due to the platform’s closed ecosystem and limited app installation options. Users typically need to configure VPN or proxy settings at the router level to protect Apple TV IPTV traffic, though some IPTV applications support built-in proxy configuration. The Infuse Pro media player, for example, includes advanced networking options that can work with SOCKS5 proxies configured through the application settings.
Fire TV Stick bypass methods leverage the device’s Android-based operating system to install VPN applications and alternative IPTV players with enhanced networking capabilities. Users can sideload VPN applications using tools like Downloader or Apps2Fire, then configure these applications to protect IPTV traffic automatically. The Cinema HD and Typhoon TV applications include built-in proxy support that can help bypass ISP blocking without requiring separate VPN installations.
Network Optimization Techniques
Network optimization techniques for overcoming ISP IPTV blocking focus on maximizing available bandwidth, minimizing latency, and implementing intelligent traffic management that can help IPTV streams maintain acceptable quality even when ISPs implement throttling or blocking measures. These techniques often work in conjunction with other bypass methods to provide comprehensive protection against various types of ISP interference.
Bandwidth allocation strategies involve configuring Quality of Service (QoS) rules that prioritize IPTV traffic over other network activities, ensuring that streaming applications receive sufficient bandwidth even during periods of high network usage. Modern routers include adaptive QoS features that can automatically identify and prioritize streaming traffic, while advanced users can configure custom QoS rules that guarantee specific bandwidth allocations for IPTV devices.
Traffic prioritization methods can help ensure that IPTV streams receive preferential treatment over less time-sensitive activities like file downloads or software updates. Gaming mode settings available on many modern routers often provide excellent optimization for IPTV streaming due to their focus on minimizing latency and maintaining consistent performance. Users can also configure custom traffic shaping rules that limit bandwidth for specific devices or applications during IPTV viewing sessions.
Connection bonding solutions allow users to combine multiple internet connections to increase total available bandwidth and provide redundancy against ISP blocking measures. Speedify and similar bonding services can aggregate cellular, WiFi, and ethernet connections to create a single high-speed connection that’s more resistant to ISP interference. These solutions are particularly valuable for users in areas with multiple ISP options or those who can combine fixed broadband with cellular data connections.
Buffer optimization techniques involve configuring IPTV applications to use larger buffer sizes that can help maintain smooth playback even when ISPs implement intermittent throttling or blocking. Most IPTV players allow users to adjust buffer settings through advanced configuration menus, with larger buffers providing better protection against temporary connection issues at the cost of increased memory usage and longer startup times.
Network monitoring tools help users identify ISP blocking attempts and optimize their bypass strategies accordingly. Applications like Wireshark, NetWorx, and GlassWire can monitor network traffic in real-time, identifying patterns that indicate ISP interference and helping users adjust their configurations for optimal performance. These tools can also help users determine which bypass methods are most effective with their specific ISP and network configuration.
Alternative Internet Solutions for IPTV Users
Switching to IPTV-Friendly ISPs
Switching to IPTV-friendly ISPs represents the most straightforward long-term solution for users experiencing persistent internet provider IPTV blocking, though this approach requires careful research and may not be feasible in areas with limited ISP competition. The process involves evaluating alternative providers based on their policies toward streaming services, network infrastructure quality, and track record of supporting unrestricted internet access.
Researching ISP policies before switching requires examining multiple sources of information including official terms of service, customer reviews, and community forums where users discuss their experiences with different providers. Many ISPs don’t explicitly state their IPTV policies in marketing materials, making it necessary to contact customer service representatives directly or consult online communities where users share real-world experiences with various providers.
Fiber-optic ISPs generally provide the best experience for IPTV users due to their superior bandwidth capacity and more modern network infrastructure. Providers like Google Fiber, Verizon FiOS, and regional fiber cooperatives typically implement fewer restrictions on streaming services because their networks can easily handle high-bandwidth IPTV traffic without experiencing congestion. Fiber providers also tend to have more progressive policies toward net neutrality and open internet access.
Municipal broadband services often provide excellent alternatives for IPTV users, as these government-operated networks typically prioritize public service over profit maximization. Cities like Chattanooga, Tennessee (EPB Fiber), Wilson, North Carolina (Greenlight), and Longmont, Colorado (NextLight) operate municipal broadband networks that generally don’t implement IPTV blocking measures and offer competitive pricing with excellent customer service.
Questions to ask potential providers should focus on specific policies and technical capabilities that affect IPTV performance:
- Do you implement any traffic shaping or throttling for streaming services?
- Are there any restrictions on the types of applications or services I can use?
- What is your policy regarding high-bandwidth usage during peak hours?
- Do you use Deep Packet Inspection or other traffic analysis technologies?
- Can you guarantee consistent speeds during evening peak usage periods?
Contract negotiation tips can help users secure better terms and protections against future policy changes. Business internet plans often include stronger service level agreements and fewer restrictions compared to residential services, though they typically cost more. Users should also negotiate for contract terms that allow cancellation without penalties if the ISP implements new restrictions that affect IPTV access.
Mobile Hotspot and 5G Solutions
Mobile hotspot and 5G solutions provide increasingly viable alternatives for IPTV users seeking to bypass traditional ISP blocking measures, offering the flexibility of cellular connectivity with improving speeds and data allowances that can support high-quality streaming. The rapid deployment of 5G networks has made cellular internet a legitimate alternative to fixed broadband for many users, particularly those in areas with limited ISP competition.
Unlimited data plan options from major cellular carriers have evolved to support serious streaming usage, though users must carefully examine the terms and conditions to understand throttling policies and network management practices. Verizon’s Get More Unlimited plan includes 50GB of premium mobile hotspot data before throttling, while T-Mobile’s Magenta MAX offers 40GB of high-speed hotspot data with unlimited smartphone usage that can be shared through hotspot functionality.
5G home internet services represent a new category of fixed wireless broadband that can provide excellent IPTV performance without the restrictions commonly implemented by traditional ISPs. T-Mobile Home Internet and Verizon 5G Home offer unlimited data plans with speeds comparable to cable internet, often without the traffic management policies that affect IPTV streaming on traditional broadband connections.
Mobile carrier IPTV policies vary significantly between providers and plan types, with some carriers implementing their own streaming restrictions while others maintain relatively open policies. AT&T has historically been more restrictive toward IPTV services due to their ownership of DirecTV, while T-Mobile and Verizon generally maintain more neutral policies toward third-party streaming services.
Cost comparison analysis between cellular and traditional broadband reveals that mobile solutions can be competitive for moderate usage patterns, particularly when factoring in the elimination of equipment rental fees and installation costs. However, users with extremely high data usage (500GB+ per month) may find cellular solutions more expensive than unlimited fixed broadband plans.
Network performance considerations for cellular IPTV include factors like tower congestion, signal strength, and carrier prioritization policies that can affect streaming quality. Users should test cellular performance at different times of day and in various locations within their homes to ensure consistent IPTV performance before canceling traditional broadband services.
Satellite Internet for IPTV
Satellite internet for IPTV has undergone revolutionary improvements with the introduction of low Earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations that offer dramatically reduced latency and increased bandwidth compared to traditional geostationary satellite services. These new satellite internet options provide viable alternatives for IPTV users in rural areas or those seeking to avoid ISP blocking measures implemented by terrestrial providers.
Starlink IPTV compatibility has exceeded expectations for many users, with the service providing sufficient bandwidth and low enough latency to support high-definition IPTV streaming. Starlink’s LEO satellite constellation operates at altitudes of approximately 550 kilometers, resulting in latency of 20-40 milliseconds that’s suitable for real-time streaming applications. The service’s unlimited data policy and lack of traditional ISP traffic management make it particularly attractive for IPTV users experiencing blocking from terrestrial providers.
Traditional satellite internet options like HughesNet and Viasat have improved their offerings significantly but still face limitations that can affect IPTV performance. These geostationary satellite services typically experience latency of 600+ milliseconds due to the distance signals must travel to satellites positioned 35,786 kilometers above Earth. While this latency doesn’t prevent IPTV streaming, it can cause delays in channel changing and interactive features.
Latency and bandwidth considerations remain critical factors when evaluating satellite internet for IPTV applications. Modern LEO satellite services like Starlink can provide latency comparable to terrestrial broadband, while traditional geostationary services may experience delays that affect user experience. Bandwidth capabilities have improved dramatically across all satellite internet options, with most services now capable of supporting multiple simultaneous HD streams.
Rural area solutions often find satellite internet to be the only viable high-speed option, making IPTV compatibility a crucial consideration for cord-cutting households. The combination of satellite internet with IPTV services can provide rural users with access to entertainment options that were previously unavailable or prohibitively expensive through traditional satellite TV services.
Weather impact mitigation strategies help satellite internet users maintain IPTV access during adverse weather conditions that can affect signal quality. Users can implement rain fade mitigation techniques like installing larger satellite dishes, using signal amplifiers, or configuring IPTV applications with larger buffers to maintain streaming during brief signal interruptions.
Legal IPTV Alternatives and Recommendations
Legitimate IPTV Service Providers
Legitimate IPTV service providers offer legal alternatives that eliminate concerns about internet provider blocking while providing comprehensive entertainment options that can satisfy most cord-cutting households. These services operate with proper licensing agreements and content distribution rights, ensuring reliable access without the legal and technical risks associated with unauthorized IPTV platforms.
YouTube TV has emerged as one of the most comprehensive legitimate IPTV alternatives, offering over 85 channels including major broadcast networks, cable channels, and premium add-ons. The service provides unlimited cloud DVR storage, supports up to six user accounts per household, and includes access to YouTube Premium content. YouTube TV’s integration with Google’s ecosystem makes it particularly attractive for users of Android devices and Google smart home products, while its robust infrastructure ensures reliable streaming without ISP interference.
Hulu + Live TV combines Disney’s extensive on-demand content library with live television streaming, offering over 75 channels plus access to Hulu’s original programming and Disney+ content. The service includes 50 hours of cloud DVR storage (expandable to 200 hours for an additional fee) and supports streaming on multiple devices simultaneously. Hulu’s content partnerships with major networks ensure access to current episodes of popular shows, making it an excellent alternative for users who want both live and on-demand content.
Sling TV provides the most flexible and affordable legitimate IPTV option, with base packages starting at $35 per month and extensive customization through add-on packages. The service offers two base packages (Sling Orange and Sling Blue) that can be combined for comprehensive channel coverage, plus specialized add-ons for sports, news, international content, and premium networks. Sling TV’s à la carte approach allows users to build customized channel lineups that match their viewing preferences without paying for unwanted content.
FuboTV focuses primarily on sports content, offering comprehensive coverage of NFL, NBA, MLB, NHL, and international soccer leagues that makes it particularly attractive for sports enthusiasts. The service includes over 100 channels in its base package, with extensive sports coverage that rivals traditional cable and satellite offerings. FuboTV’s cloud DVR functionality and multi-screen viewing capabilities make it excellent for households with multiple sports fans who want to watch different games simultaneously.
AT&T TV Now (formerly DirecTV Now) provides access to traditional television programming through internet streaming, offering multiple package tiers with different channel lineups and pricing options. The service includes access to HBO Max content and provides extensive on-demand libraries from major networks. While AT&T TV Now has faced some reliability issues and price increases, it remains a legitimate option for users who want traditional television programming without satellite installation requirements.
Streaming Platform Combinations
Streaming platform combinations can provide comprehensive entertainment coverage that rivals traditional television services while maintaining complete legitimacy and avoiding ISP IPTV blocking concerns. By strategically combining multiple streaming services, users can access virtually all available content while often spending less than traditional cable or satellite television subscriptions.
Netflix, Amazon Prime, and Disney+ bundles form the foundation of most cord-cutting strategies, providing access to the vast majority of popular movies and television shows. Netflix offers the largest library of original content and international programming, Amazon Prime Video includes recent movies and Amazon’s growing collection of original series, while Disney+ provides access to Disney, Marvel, Star Wars, and National Geographic content. The combined cost of these three services typically ranges from $25-35 per month, significantly less than most cable television packages.
Free streaming services can supplement paid subscriptions to provide additional content without increasing monthly costs. Tubi offers thousands of movies and TV shows with advertising support, Crackle provides Sony Pictures content, and Pluto TV offers live television channels and on-demand content. IMDb TV (now Amazon Freevee) includes popular movies and original programming, while Roku Channel aggregates free content from multiple sources with an easy-to-navigate interface.
Network-specific applications provide access to current episodes and extensive back catalogs from major television networks. CBS All Access (now Paramount+) includes live CBS programming and exclusive original series, NBC Peacock offers NBCUniversal content with both free and premium tiers, and ABC iView provides access to ABC programming and Disney-owned content. These network apps often include live streaming of local broadcasts in major markets, providing access to news and sports programming.
Cost-effective streaming strategies involve rotating subscriptions based on content availability and viewing patterns. Users can subscribe to services when new seasons of favorite shows are released, then cancel and switch to different services to maximize content variety while minimizing monthly costs. Annual subscription discounts offered by many services can provide significant savings for users who commit to longer-term subscriptions.
International content access through legitimate streaming services has expanded dramatically, with platforms like Netflix offering extensive international programming, Acorn TV specializing in British content, and Walter Presents providing European television series with subtitles. These services provide legal access to international content that was previously only available through unauthorized IPTV services.
Preventing Future IPTV Blocking Issues
Choosing the Right Internet Plan
Choosing the right internet plan represents a proactive approach to minimizing internet provider IPTV blocking issues, requiring careful evaluation of ISP policies, technical specifications, and contract terms that can affect streaming performance and access rights. The selection process involves balancing cost considerations with performance requirements while ensuring that chosen plans provide sufficient protection against future blocking measures.
Unlimited data requirements have become essential for IPTV users, as streaming high-definition content can consume 3-7 GB per hour, with 4K streams using 15-25 GB per hour. Households with multiple IPTV users can easily exceed 1TB of monthly data usage, making unlimited plans necessary to avoid overage charges or throttling. Users should carefully examine ISP definitions of “unlimited” service, as many providers implement fair usage policies or network management practices that can affect heavy streaming users.
Speed recommendations for IPTV depend on the number of simultaneous streams and desired video quality. A single HD stream requires 5-8 Mbps of consistent bandwidth, while 4K streams need 25-35 Mbps. Households should calculate their maximum simultaneous streaming requirements and add 50% overhead to account for other internet activities and network inefficiencies. Fiber internet plans typically provide the most consistent speeds with minimal variation between advertised and actual performance.
Contract terms to avoid include provisions that give ISPs broad discretion to implement traffic management, throttling, or blocking measures. Users should be particularly wary of contracts that include vague language about “network optimization,” “fair usage,” or “reasonable network management” without specific definitions or limitations. Month-to-month plans often provide more flexibility than long-term contracts, allowing users to switch providers if blocking issues develop.
Business vs. residential plans can significantly impact IPTV access and performance. Business internet plans typically include stronger service level agreements, fewer restrictions on usage patterns, and priority customer support that can help resolve blocking issues more quickly. While business plans cost more than residential services, they often provide better protection against traffic management practices that affect IPTV streaming.
Upload speed considerations are often overlooked but can affect IPTV performance, particularly for users who share content or use cloud-based DVR services. Many ISPs offer asymmetric plans with much lower upload speeds than download speeds, which can create bottlenecks for interactive IPTV features. Symmetric fiber plans that provide equal upload and download speeds offer the best performance for advanced IPTV applications.
Network Security and Privacy
Network security and privacy measures play crucial roles in preventing ISP IPTV blocking while protecting users from potential legal and security risks associated with streaming activities. Implementing comprehensive security practices helps maintain anonymity, prevents ISP monitoring, and reduces the likelihood of triggering automated blocking systems that target suspicious network behavior.
Protecting streaming activity requires implementing multiple layers of security that prevent ISPs from analyzing traffic patterns and identifying IPTV usage. VPN encryption provides the most comprehensive protection by creating encrypted tunnels that hide all internet activity from ISP monitoring. Users should select VPN services that maintain strict no-logging policies and use strong encryption protocols like OpenVPN or WireGuard that resist traffic analysis attempts.
DNS over HTTPS (DoH) and DNS over TLS (DoT) protocols prevent ISPs from monitoring DNS queries that can reveal IPTV service usage. Modern browsers like Firefox and Chrome support DoH by default, while operating systems like Windows 11 and macOS include built-in DoT support. Configuring secure DNS protocols prevents ISPs from using DNS monitoring to identify and block IPTV services.
Encryption best practices extend beyond VPN usage to include securing local network communications and preventing unauthorized access to IPTV devices. Users should ensure that all WiFi networks use WPA3 encryption (or WPA2 if WPA3 isn’t available) with strong passwords that resist brute-force attacks. Guest networks should be configured for IPTV devices to isolate streaming traffic from other household internet activities.
Anonymous browsing techniques help prevent ISPs from building profiles of user behavior that could trigger blocking measures. Tor browser provides the highest level of anonymity but may be too slow for IPTV streaming. Privacy-focused browsers like Brave or Firefox with privacy extensions can provide good protection for IPTV-related web browsing without significantly impacting performance.
Router security configurations should include disabling unnecessary services, changing default passwords, and implementing access controls that prevent unauthorized network access. Firmware updates should be applied regularly to address security vulnerabilities that could be exploited by ISPs or malicious actors. Network segmentation using VLANs can isolate IPTV devices from other network resources, reducing the impact of potential security breaches.
Staying Updated on ISP Policies
Staying updated on ISP policies requires ongoing monitoring of terms of service changes, industry developments, and regulatory updates that can affect IPTV access rights. ISPs frequently modify their policies and network management practices, making it essential for users to stay informed about changes that could impact their streaming activities.
Monitoring terms of service changes involves regularly reviewing ISP policy documents and watching for notifications about service modifications. Many ISPs send policy change notifications through email or postal mail, but these communications often use technical language that obscures the practical implications for IPTV users. Consumer advocacy websites like the Electronic Frontier Foundation (EFF) often provide plain-language explanations of ISP policy changes and their potential impacts.
Industry news and regulation updates can provide early warning about potential blocking measures or policy changes affecting IPTV access. Cord-cutting forums and streaming communities on platforms like Reddit often discuss ISP blocking experiences and share information about effective countermeasures. Technology news websites like Ars Technica, The Verge, and TechCrunch regularly cover ISP policy developments and net neutrality issues.
Community forums and resources provide valuable real-world information about ISP blocking experiences and effective solutions. DSLReports maintains extensive forums where users discuss ISP performance and policies, while Reddit communities like r/cordcutters and r/IPTV share current information about blocking issues and workarounds. These communities often provide more current and practical information than official ISP communications.
Legal advocacy organizations like the Electronic Frontier Foundation, Free Press, and Public Knowledge monitor ISP practices and advocate for consumer rights. These organizations often provide resources for reporting ISP blocking issues and can offer guidance on legal options for addressing service restrictions. Supporting these organizations through donations or membership can help strengthen advocacy efforts that benefit all internet users.
Regulatory monitoring involves tracking Federal Communications Commission (FCC) proceedings, state-level legislation, and court cases that affect ISP regulation and net neutrality enforcement. The FCC’s website provides access to official proceedings and public comments related to internet regulation, while legal databases like Justia offer access to court decisions affecting ISP practices and consumer rights.
Troubleshooting Common IPTV Blocking Problems
Connection and Streaming Issues
Connection and streaming issues caused by internet provider IPTV blocking often manifest as seemingly random problems that can be difficult to distinguish from normal network issues or service outages. Effective troubleshooting requires systematic testing to identify the root cause of problems and determine whether ISP interference is responsible for degraded performance.
Buffer wheel solutions address one of the most common symptoms of ISP IPTV blocking, where streams pause frequently to load additional content despite apparently adequate internet speeds. When buffering occurs consistently with IPTV services but not with other streaming platforms like YouTube or Netflix, this pattern strongly suggests ISP throttling or blocking. Users can often resolve buffering issues by reducing stream quality settings, increasing application buffer sizes, or implementing VPN connections that bypass ISP traffic management.
Systematic buffer troubleshooting involves testing different video quality settings to determine if buffering occurs at all resolution levels or only with high-definition streams. If 720p streams work reliably while 1080p streams buffer constantly, this suggests bandwidth throttling rather than complete blocking. Users should also test buffering patterns at different times of day, as ISP traffic management often intensifies during peak evening hours when network congestion is highest.
Audio/video sync problems can indicate ISP interference with IPTV streams, particularly when sync issues occur consistently with specific services or during certain time periods. ISP traffic shaping can introduce variable delays that disrupt the timing relationship between audio and video components of streams. Users experiencing sync problems should test the same content through VPN connections to determine if ISP interference is responsible for timing issues.
Channel loading failures represent another common symptom of ISP IPTV blocking, where channel lists load successfully but individual streams fail to start or display error messages. This pattern often indicates that ISPs are blocking specific streaming servers while allowing access to IPTV service websites and authentication systems. Users can often resolve loading failures by switching to alternative server locations within their IPTV service or using VPN connections to bypass ISP blocking.
App crash troubleshooting requires examining whether crashes occur with all IPTV applications or only specific ones, as ISP blocking can sometimes trigger application instability. Deep Packet Inspection systems used by some ISPs can interfere with application protocols in ways that cause unexpected crashes or freezes. Users should test multiple IPTV applications to determine if crashes are application-specific or affect all streaming software.
Device-Specific Problems
Device-specific problems related to ISP IPTV blocking often require tailored troubleshooting approaches that account for the unique networking capabilities and limitations of different streaming hardware platforms. Each device category presents distinct challenges and opportunities for implementing effective solutions to blocking-related issues.
Smart TV connectivity issues frequently stem from limited networking options and restricted software environments that make it difficult to implement blocking countermeasures. Many smart TV platforms don’t support VPN applications or advanced proxy configurations, requiring users to implement solutions at the router level or through external streaming devices. Samsung Tizen and LG webOS smart TVs often experience DNS-related blocking that can be resolved by changing DNS server settings in the network configuration menu.
Smart TV troubleshooting steps should begin with testing the same IPTV service on different devices to confirm that problems are TV-specific rather than network-wide. Users should also test different network connections, such as switching from WiFi to ethernet or using mobile hotspot connections, to determine if the smart TV’s network interface is experiencing ISP-specific blocking. Factory reset procedures can sometimes resolve persistent connectivity issues caused by corrupted network settings or cached blocking responses.
Android box configuration problems often relate to VPN or proxy settings that aren’t properly configured for the specific IPTV applications being used. Android TV boxes offer more flexibility than smart TVs but require careful attention to application-level networking settings. Users should verify that VPN applications are configured to start automatically and protect all network traffic, not just web browsing. Split tunneling settings in VPN applications can sometimes interfere with IPTV streaming by routing some traffic through VPN connections while leaving other traffic unprotected.
Android box optimization techniques include configuring applications to use specific DNS servers, adjusting buffer settings for optimal performance, and ensuring that background applications aren’t consuming bandwidth needed for IPTV streaming. Developer options in Android settings can provide access to advanced networking features that help optimize IPTV performance, though users should be cautious about modifying system-level settings without understanding their implications.
iOS/iPhone streaming difficulties often result from Apple’s restrictive app ecosystem and limited support for advanced networking configurations. iPhone users typically need to rely on VPN applications or router-level solutions to bypass ISP IPTV blocking, as iOS doesn’t support system-level proxy configurations for most applications. AirPlay streaming from iOS devices to Apple TV or other compatible devices can sometimes bypass blocking that affects direct streaming applications.
Windows/Mac computer solutions offer the most flexibility for implementing IPTV blocking countermeasures, as desktop operating systems support comprehensive VPN clients, proxy configurations, and network monitoring tools. Users can implement system-wide VPN protection, configure application-specific proxy settings, or use virtual machine environments to isolate IPTV streaming from other computer activities.
Network Performance Optimization
Network performance optimization for overcoming ISP IPTV blocking involves implementing comprehensive strategies that maximize available bandwidth, minimize latency, and ensure consistent streaming quality even when ISPs implement traffic management or throttling measures. These optimization techniques often work synergistically with blocking countermeasures to provide the best possible IPTV experience.
Internet speed requirements for IPTV streaming extend beyond simple bandwidth calculations to include considerations of consistency, latency, and packet loss that can significantly impact streaming quality. While a 1080p stream may only require 8 Mbps of bandwidth, achieving reliable streaming often requires 15-20 Mbps of available capacity to accommodate network overhead, buffering requirements, and temporary congestion. Jitter and packet loss measurements are often more important than raw bandwidth for IPTV performance, as even small amounts of packet loss can cause visible artifacts and buffering.
Speed testing methodologies should include both general internet speed tests and IPTV-specific performance measurements to identify ISP throttling or blocking. Users should conduct speed tests at multiple times throughout the day to identify patterns that suggest traffic management policies. Streaming-specific speed tests that measure performance while actually streaming video content can provide more accurate assessments of IPTV performance than general bandwidth tests.
WiFi vs. ethernet connections can significantly impact IPTV performance, particularly in households with multiple wireless devices competing for bandwidth. Ethernet connections provide more consistent performance and lower latency than WiFi, making them preferable for stationary IPTV devices like smart TVs or dedicated streaming boxes. When ethernet connections aren’t practical, users should ensure that IPTV devices connect to 5GHz WiFi bands rather than more congested 2.4GHz networks.
Router placement and settings optimization can dramatically improve IPTV performance by reducing interference and maximizing signal strength. Routers should be positioned centrally within homes and elevated above floor level to minimize obstacles that can interfere with wireless signals. Channel selection for WiFi networks should avoid congested frequencies, with tools like WiFi Analyzer helping identify optimal channel assignments for specific environments.
Interference reduction techniques include identifying and eliminating sources of wireless interference that can degrade IPTV streaming performance. Microwave ovens, baby monitors, and Bluetooth devices can all interfere with WiFi signals, particularly on 2.4GHz frequencies. Mesh networking systems can help eliminate dead zones and provide consistent coverage throughout larger homes, though users should ensure that mesh systems support band steering and load balancing features that optimize performance for streaming applications.
Quality of Service (QoS) configuration allows users to prioritize IPTV traffic over other network activities, ensuring that streaming applications receive adequate bandwidth even when other devices are consuming network resources. Modern routers often include adaptive QoS features that automatically identify and prioritize streaming traffic, while advanced users can configure custom QoS rules that guarantee specific bandwidth allocations for IPTV devices.
Cost Analysis: IPTV vs. Traditional TV Services
Financial Benefits of IPTV
Financial benefits of IPTV extend far beyond simple monthly subscription savings, encompassing reduced equipment costs, elimination of installation fees, and increased flexibility that can result in substantial long-term savings compared to traditional cable and satellite television services. Understanding the complete cost structure helps consumers make informed decisions about cord-cutting while accounting for potential expenses related to internet provider IPTV blocking countermeasures.
Monthly cost comparisons reveal dramatic differences between IPTV services and traditional television providers. The average cable television bill in the United States exceeds $120 per month, while comprehensive IPTV solutions can provide similar channel lineups for $30-60 per month. YouTube TV at $65 per month includes over 85 channels plus unlimited cloud DVR, while Sling TV packages start at $35 per month for 30+ channels. Even when combined with premium add-ons and multiple streaming services, most IPTV solutions cost significantly less than traditional cable packages.
Equipment rental savings represent a significant but often overlooked advantage of IPTV services. Traditional cable and satellite providers typically charge $10-20 per month for each set-top box, with additional fees for DVR functionality and premium features. A household with three televisions might pay $40-60 per month in equipment rental fees alone, while IPTV services work with existing smart TVs, streaming devices, or inexpensive Android boxes that users own outright.
Installation and activation fees charged by traditional providers can add $100-300 to the initial cost of service, while IPTV services typically require no professional installation or activation fees. Users can begin streaming immediately after subscribing, without waiting for technician appointments or dealing with complex installation procedures. This immediate activation also provides flexibility for users who need to relocate frequently or want to test services before committing to long-term contracts.
Contract flexibility advantages allow IPTV users to adjust their service levels based on changing needs and budgets without facing early termination fees or contract extensions. Most IPTV services offer month-to-month subscriptions that can be cancelled or modified at any time, while traditional providers often require 1-2 year contracts with significant penalties for early cancellation. This flexibility is particularly valuable for users who experience seasonal income variations or want to experiment with different service combinations.
International content access through IPTV services often costs significantly less than specialized international packages offered by traditional providers. Cable and satellite companies typically charge $20-50 per month for international channel packages with limited content, while IPTV services can provide extensive international programming for a fraction of these costs. Users interested in content from multiple countries can often access diverse programming through IPTV services for less than the cost of a single international package from traditional providers.
Hidden Costs of ISP Blocking Solutions
Hidden costs of ISP blocking solutions can significantly impact the overall economics of IPTV cord-cutting, potentially reducing or eliminating the financial advantages that initially motivate users to abandon traditional television services. Understanding these additional expenses helps users budget appropriately and make informed decisions about which blocking countermeasures provide the best value for their specific situations.
VPN subscription expenses represent the most common additional cost for users experiencing internet provider IPTV blocking, with premium VPN services typically costing $5-15 per month depending on subscription length and feature requirements. Annual VPN subscriptions often provide better value than monthly plans, with services like ExpressVPN costing $8.32 per month when paid annually versus $12.95 monthly. However, users should factor in the risk that VPN services may become less effective over time as ISPs develop more sophisticated blocking detection methods.
Multiple VPN service costs may be necessary for users who find that single VPN providers don’t consistently bypass their ISP’s blocking measures. Some users maintain subscriptions to 2-3 different VPN services to ensure reliable access, potentially adding $15-30 per month to their IPTV costs. VPN rotation strategies can help minimize these costs by maintaining one primary subscription and adding secondary services only when needed, though this approach requires more active management.
Router upgrade costs can represent significant one-time expenses for users who need more advanced networking equipment to implement effective blocking countermeasures. VPN-compatible routers with sufficient processing power to handle encryption without degrading performance typically cost $150-400, while mesh networking systems that provide comprehensive coverage can cost $300-600. Users with older routers may find that their existing equipment can’t support the advanced features needed for effective IPTV protection.
Professional installation expenses for complex networking solutions can add $100-300 to the cost of implementing IPTV blocking countermeasures. While many users can configure VPN routers and mesh networks themselves, others may prefer professional installation to ensure optimal performance and security. Networking consultants who specialize in IPTV optimization typically charge $75-150 per hour for configuration and troubleshooting services.
Alternative internet service fees represent potentially substantial ongoing costs for users who switch to more expensive ISPs or add secondary internet connections to bypass blocking. Fiber internet services that don’t implement IPTV blocking often cost $20-50 more per month than basic cable internet, while 5G home internet services may include data usage charges that exceed unlimited cable internet costs for heavy streaming households.
Technical support expenses can accumulate over time as users encounter blocking issues that require professional assistance to resolve. Remote technical support services specializing in IPTV troubleshooting typically charge $50-100 per incident, while ongoing support contracts that provide unlimited assistance may cost $10-25 per month. Users who aren’t comfortable with technical troubleshooting may find these support costs necessary for maintaining reliable IPTV access.
Opportunity costs of time spent researching, implementing, and maintaining blocking countermeasures should be considered when evaluating the true cost of IPTV solutions. Users may spend 5-10 hours initially setting up VPN services and optimizing their networks, plus ongoing time for troubleshooting and maintenance. For users whose time has significant value, these opportunity costs can offset some of the financial savings achieved through cord-cutting.
Future of IPTV and ISP Blocking
Industry Trends and Predictions
Industry trends and predictions regarding internet provider IPTV blocking suggest an escalating technological arms race between ISPs implementing increasingly sophisticated blocking measures and users developing more advanced countermeasures. The evolution of this conflict will be shaped by regulatory changes, technological developments, and shifting business models that affect both ISP incentives and user capabilities.
5G impact on IPTV delivery promises to fundamentally alter the landscape of internet-based television streaming by providing alternative connectivity options that bypass traditional ISP infrastructure. 5G networks operated by cellular carriers often have different business models and regulatory frameworks compared to fixed broadband ISPs, potentially offering more neutral policies toward IPTV services. The increased bandwidth and reduced latency of 5G networks make them viable alternatives for high-quality IPTV streaming, reducing user dependence on traditional ISPs that implement blocking measures.
Edge computing integration with 5G networks will enable content delivery networks (CDNs) to cache IPTV content closer to end users, reducing bandwidth requirements and improving streaming quality. This technological advancement may reduce ISP incentives to block IPTV services by minimizing the network impact of streaming traffic. Multi-access edge computing (MEC) deployments will allow IPTV providers to deliver content through cellular networks with performance comparable to or better than traditional broadband connections.
Regulatory changes on the horizon include potential federal legislation that could strengthen net neutrality protections and limit ISP ability to block or throttle specific types of content. State-level net neutrality laws in states like California have already created patchwork regulations that affect ISP practices, while federal policy changes could establish nationwide standards for internet traffic management. The outcome of ongoing legal challenges to ISP blocking practices will likely influence future regulatory approaches.
International regulatory harmonization efforts may create global standards for internet traffic management that limit ISP blocking capabilities. European Union regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and Digital Services Act are influencing global internet governance practices, while trade agreements increasingly include provisions related to internet freedom and cross-border data flows that could affect IPTV access.
Technology advancement effects include the development of new protocols and encryption methods that make it increasingly difficult for ISPs to identify and block IPTV traffic. HTTP/3 and QUIC protocols provide enhanced encryption and performance that can help IPTV services evade detection, while decentralized networking technologies like blockchain-based content delivery may create new distribution models that are inherently resistant to ISP blocking.
Artificial intelligence integration in both ISP blocking systems and user countermeasures will create an increasingly sophisticated technological competition. Machine learning algorithms can help ISPs identify IPTV traffic patterns more accurately, while AI-powered VPN services can automatically adapt to blocking attempts and optimize performance in real-time.
Emerging Technologies and Solutions
Emerging technologies and solutions for combating ISP IPTV blocking leverage cutting-edge networking innovations, cryptographic advances, and distributed computing architectures that promise to make content blocking increasingly difficult and expensive for ISPs to implement effectively. These technological developments represent the next generation of tools available to users seeking unrestricted access to IPTV content.
Blockchain-based streaming platforms utilize distributed ledger technologies to create decentralized content delivery networks that are inherently resistant to traditional blocking methods. Theta Network and similar blockchain streaming platforms distribute content across thousands of nodes operated by users, making it impossible for ISPs to block access by targeting specific servers or IP addresses. These platforms often include cryptocurrency incentives that encourage users to participate in content distribution, creating self-sustaining networks that become more robust as they grow.
Decentralized content delivery through peer-to-peer (P2P) protocols eliminates single points of failure that ISPs can target for blocking. BitTorrent-based streaming technologies allow IPTV content to be distributed across multiple sources simultaneously, with users downloading different segments from various peers. This approach makes blocking extremely difficult because ISPs would need to identify and block thousands of individual connections rather than targeting specific streaming servers.
Mesh networking technologies enable users to create local networks that can share internet connections and route traffic around ISP blocking measures. Community mesh networks in urban areas can provide alternative connectivity that bypasses traditional ISP infrastructure entirely, while satellite mesh networks using services like Starlink can create redundant connections that maintain IPTV access even when terrestrial ISPs implement blocking.
Advanced encryption protocols like WireGuard and Shadowsocks provide faster and more secure VPN connections that are harder for ISPs to detect and block. Obfuscation technologies can make VPN traffic appear as regular web browsing, while domain fronting techniques route traffic through major cloud services that ISPs are reluctant to block due to potential collateral damage to legitimate services.
AI-powered traffic optimization systems can automatically adapt to ISP blocking attempts by analyzing network performance in real-time and adjusting routing, encryption, and protocol settings to maintain optimal IPTV streaming quality. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns in ISP blocking behavior and proactively implement countermeasures before users experience service degradation.
Quantum networking technologies, while still in early development, promise to provide theoretically unbreakable encryption that could make ISP traffic analysis impossible. Quantum key distribution and quantum internet protocols may eventually provide IPTV users with absolute protection against ISP monitoring and blocking, though these technologies remain years away from practical implementation.
Software-defined networking (SDN) tools allow advanced users to create programmable networks that can automatically respond to blocking attempts by rerouting traffic through alternative paths. Network function virtualization (NFV) enables users to deploy sophisticated networking capabilities using standard hardware, potentially making enterprise-grade blocking countermeasures accessible to residential users.
Expert Tips and Best Practices
Professional Recommendations
Professional recommendations from networking experts, cybersecurity specialists, and industry professionals provide valuable insights for users seeking to overcome internet provider IPTV blocking while maintaining security, performance, and legal compliance. These expert perspectives reflect years of experience dealing with ISP restrictions and represent best practices developed through real-world testing and implementation.
Network security professionals consistently emphasize the importance of implementing defense in depth strategies that combine multiple blocking countermeasures rather than relying on single solutions. Cybersecurity expert recommendations include using VPN services with kill switch functionality that automatically disconnects internet access if VPN protection fails, preventing ISPs from detecting unprotected IPTV traffic during connection interruptions. Multi-factor authentication for VPN and IPTV accounts helps protect against unauthorized access that could compromise user privacy or trigger ISP blocking measures.
Industry specialists recommend maintaining operational security (OPSEC) practices that minimize the digital footprint associated with IPTV usage. This includes using dedicated email addresses for IPTV service registrations, separate payment methods that don’t link to primary financial accounts, and compartmentalized browsing that isolates IPTV-related web activity from other online activities. Privacy-focused browsers with tracking protection help prevent ISPs from building behavioral profiles that could trigger blocking measures.
Telecommunications engineers emphasize the importance of network monitoring to identify ISP blocking attempts and measure the effectiveness of countermeasures. Professional-grade monitoring tools like PRTG Network Monitor or SolarWinds NPM can provide detailed insights into network performance and help identify patterns that indicate ISP interference. Baseline performance measurements taken before implementing blocking countermeasures provide reference points for evaluating solution effectiveness.
Legal professionals specializing in telecommunications law recommend documenting ISP blocking incidents to support potential legal challenges or regulatory complaints. Evidence collection should include speed test results, connection logs, and comparative performance data that demonstrate ISP discrimination against IPTV traffic. Consumer protection attorneys suggest maintaining detailed records of service degradation and any communications with ISP customer service regarding blocking issues.
Technical consultants who specialize in IPTV optimization recommend redundant connectivity solutions that provide backup internet access when primary ISPs implement blocking measures. Dual-WAN configurations using different ISP technologies (cable + fiber, or broadband + cellular) can automatically failover to unblocked connections. Load balancing across multiple internet connections can also help distribute IPTV traffic to avoid triggering bandwidth-based blocking thresholds.
Community Solutions and Resources
Community solutions and resources developed by IPTV users and cord-cutting enthusiasts provide practical, tested approaches to overcoming ISP IPTV blocking that often prove more effective than commercial solutions. These community-driven resources leverage collective knowledge and experience to develop innovative countermeasures and share real-time information about ISP blocking activities.
Online forums and communities serve as invaluable resources for users seeking current information about ISP blocking patterns and effective countermeasures. Reddit communities like r/cordcutters, r/IPTV, and r/VPN maintain active discussions about blocking issues and solution sharing. DSLReports forums provide detailed technical discussions about ISP practices and networking solutions, while Kodi community forums offer specialized advice for users of popular IPTV software platforms.
User-generated solutions often provide more practical and cost-effective approaches than commercial alternatives. Community-developed scripts for router firmware like DD-WRT and OpenWrt can automate VPN connections and traffic routing for optimal IPTV performance. Open-source VPN configurations shared by community members often include optimized settings for specific ISPs and geographic regions that provide better performance than default configurations.
Crowdsourced troubleshooting through community platforms enables users to quickly identify and resolve blocking issues by leveraging collective experience. Discord servers and Telegram groups dedicated to IPTV provide real-time support and information sharing, while GitHub repositories host community-maintained lists of working VPN servers, proxy configurations, and blocking countermeasures.
Peer support networks help users navigate the technical complexities of implementing blocking countermeasures through mentorship and guided assistance. Community tutorials and video guides created by experienced users provide step-by-step instructions for configuring VPN routers, optimizing network settings, and troubleshooting common issues. Local meetup groups in major metropolitan areas sometimes organize workshops and training sessions for cord-cutting enthusiasts.
Collaborative testing initiatives organized by community members help identify effective countermeasures and track ISP blocking patterns across different geographic regions and provider networks. Crowdsourced speed testing projects collect performance data from users implementing various blocking countermeasures, while ISP blocking databases maintained by community volunteers track which providers implement restrictions and which solutions prove most effective.
Resource sharing platforms enable community members to pool resources for expensive solutions like premium VPN services or specialized networking equipment. Group buying initiatives can reduce the cost of annual VPN subscriptions, while equipment lending libraries allow users to test different router configurations before making purchase decisions. Knowledge sharing wikis maintained by community volunteers provide comprehensive guides covering everything from basic VPN setup to advanced networking configurations.
Frequently Asked Questions About Internet Provider IPTV Blocking
Is it legal to bypass ISP IPTV blocking?
The legality of bypassing ISP IPTV blocking depends on several factors including the specific methods used, the nature of the content being accessed, applicable local laws, and the terms of service agreements with your ISP. In most jurisdictions, using VPNs, proxy servers, or alternative DNS services to access legal content is perfectly legal, as these tools serve legitimate privacy and security purposes beyond circumventing ISP restrictions.
VPN usage legality varies by country, with most Western democracies allowing unrestricted VPN use for privacy protection and accessing geo-restricted content. The United States, Canada, United Kingdom, and European Union countries generally permit VPN usage, though some countries like China, Russia, and Iran have implemented restrictions or bans on VPN services. Users should research local laws before implementing VPN solutions for bypassing ISP blocking.
Terms of service considerations may create contractual restrictions on bypassing ISP blocking measures, even when such activities are otherwise legal. Some ISPs include provisions in their service agreements that prohibit using VPNs or other tools to circumvent network management practices. However, courts have sometimes found such terms to be unenforceable when they conflict with consumer rights or net neutrality principles.
Content legality remains the primary legal consideration, as bypassing ISP blocking to access copyrighted content without proper licensing can still constitute copyright infringement regardless of the technical methods used. Users should ensure that any IPTV services they access have appropriate licensing agreements and distribution rights for the content they provide.
Can my ISP see what IPTV content I’m watching?
ISP visibility into IPTV content depends on the specific technologies and protocols used by both the ISP and the IPTV service, with unencrypted connections providing ISPs with extensive information about viewing habits while properly encrypted connections can hide content details from ISP monitoring systems.
Deep Packet Inspection capabilities used by many ISPs can analyze unencrypted internet traffic to identify specific IPTV services, channels, and even individual programs being watched. ISPs using DPI technology can build detailed profiles of user viewing habits, including preferred content types, viewing schedules, and bandwidth consumption patterns. This information can be used for traffic management decisions, marketing purposes, or shared with third parties depending on ISP privacy policies.
Encrypted IPTV connections using HTTPS, VPN tunnels, or other encryption protocols prevent ISPs from seeing specific content details, though they may still be able to identify that IPTV streaming is occurring based on traffic patterns, bandwidth usage, and connection destinations. Metadata analysis can reveal information about streaming duration, data volumes, and server locations even when content details remain encrypted.
VPN protection provides the most comprehensive privacy protection by encrypting all internet traffic and routing it through VPN servers, making it impossible for ISPs to determine what content is being accessed. However, ISPs can still see that VPN connections are being used and may be able to estimate total bandwidth consumption for traffic management purposes.
Will using a VPN slow down my IPTV streaming?
VPN impact on IPTV streaming speed varies significantly based on VPN service quality, server locations, encryption protocols, and network conditions, with premium VPN services often providing minimal speed reduction while budget services may cause substantial performance degradation that affects streaming quality.
Typical speed reduction with quality VPN services ranges from 10-30% of baseline internet speeds, which is usually sufficient to maintain high-definition IPTV streaming for users with adequate bandwidth. ExpressVPN and NordVPN consistently demonstrate minimal speed impact in independent testing, while budget VPN services may reduce speeds by 50% or more due to overcrowded servers and inferior infrastructure.
Server location impact significantly affects VPN performance, with nearby servers typically providing better speeds than distant locations. Users should select VPN servers within their country or region when possible, though accessing geo-restricted content may require connecting to servers in specific countries that could increase latency and reduce speeds.
Protocol optimization can help minimize VPN speed impact through selection of efficient encryption protocols like WireGuard or IKEv2 that provide better performance than older protocols like OpenVPN. Many premium VPN services automatically select optimal protocols based on network conditions and device capabilities.
Router-level VPN considerations may experience greater speed reduction due to the processing limitations of consumer router hardware. Users implementing VPN connections at the router level should ensure their hardware has sufficient CPU power to handle encryption without creating bottlenecks that affect all network traffic.
How can I tell if my ISP is throttling IPTV specifically?
Identifying ISP IPTV throttling requires systematic testing that compares IPTV performance with other types of internet traffic to determine if streaming services are being specifically targeted for bandwidth reduction or quality degradation.
Comparative speed testing provides the most reliable method for detecting IPTV throttling by measuring performance differences between IPTV streaming and other internet activities. Users should conduct speed tests using general testing tools like Speedtest.net while simultaneously streaming IPTV content to identify discrepancies that suggest throttling. Streaming-specific speed tests that measure actual video delivery performance often provide more accurate assessments than general bandwidth tests.
VPN testing methodology involves comparing IPTV performance with and without VPN connections to determine if encryption bypasses throttling measures. If IPTV streams perform significantly better through VPN connections, this strongly indicates ISP throttling of unencrypted streaming traffic. Users should test multiple VPN server locations to ensure consistent results and rule out server-specific performance issues.
Time-based analysis can reveal throttling patterns that correlate with network congestion periods or ISP traffic management policies. Users should monitor IPTV performance at different times throughout the day, with particular attention to peak evening hours when ISPs commonly implement traffic shaping measures. Consistent degradation during specific time periods suggests intentional throttling rather than random network issues.
Protocol testing involves experimenting with different streaming protocols and ports to determine if throttling targets specific technical characteristics of IPTV traffic. Users can test whether changing from HTTP to HTTPS streaming, using alternative ports, or switching between different IPTV applications affects performance in ways that suggest protocol-specific throttling.
What’s the best VPN for unblocking IPTV services?
The best VPN for unblocking IPTV services depends on specific user requirements including streaming quality needs, device compatibility, budget constraints, and geographic location, though several premium services consistently demonstrate superior performance for IPTV applications.
ExpressVPN frequently ranks as the top choice for IPTV users due to its extensive server network spanning 94 countries, consistently high speeds, and specialized streaming servers optimized for video content. The service’s MediaStreamer feature provides Smart DNS functionality for devices that don’t support VPN applications, while split tunneling allows users to route only IPTV traffic through VPN connections while maintaining direct connections for other activities.
NordVPN offers excellent value for IPTV users with features specifically designed for streaming applications. The service’s SmartPlay technology automatically selects optimal servers for streaming content, while dedicated IP addresses reduce the likelihood of being blocked by streaming services that detect shared VPN IP addresses. Double VPN encryption provides enhanced security for users concerned about ISP monitoring.
Surfshark provides exceptional value for households with multiple IPTV devices through its unlimited simultaneous connections policy and competitive pricing. The service’s CleanWeb feature blocks ads and trackers that can interfere with IPTV performance, while Camouflage Mode makes VPN traffic appear as regular browsing to ISPs using advanced detection methods.
CyberGhost specializes in streaming applications with dedicated streaming servers labeled for specific services and geographic regions. The service provides detailed server information including current load and performance metrics, helping users select optimal connections for IPTV streaming.
Server network considerations should prioritize VPN services with extensive server coverage in regions relevant to desired content, as well as sufficient server capacity to maintain high speeds during peak usage periods. Bandwidth limitations and connection limits can significantly impact IPTV performance, making unlimited services preferable for heavy streaming users.
Can I get in trouble for using blocked IPTV services?
Legal consequences of using blocked IPTV services depend primarily on the nature of the content being accessed rather than the technical methods used to bypass ISP blocking, with users of legitimate services facing minimal legal risk while those accessing unauthorized content may face copyright infringement liability.
Copyright infringement risks represent the primary legal concern for IPTV users, particularly those accessing services that distribute premium content without proper licensing agreements. DMCA takedown notices sent to ISPs can result in service warnings or termination for users accessing copyrighted content, while repeat infringement may lead to permanent service suspension or legal action by content creators.
ISP terms of service violations may result in service warnings, throttling, or account termination for users who bypass blocking measures in violation of their service agreements. However, ISPs rarely pursue aggressive enforcement against users who access legitimate content through VPNs or other privacy tools, as such actions could trigger regulatory scrutiny and customer backlash.
Criminal liability for IPTV usage is extremely rare and typically limited to cases involving commercial-scale copyright infringement or distribution of unauthorized content. Personal use of IPTV services, even unauthorized ones, rarely results in criminal prosecution, though users may face civil liability for copyright infringement.
Geographic legal variations create different risk profiles for IPTV users depending on local copyright enforcement practices and internet governance policies. European users generally face stronger privacy protections and more limited ISP monitoring, while users in countries with strict copyright enforcement may face greater risks from accessing unauthorized content.
Are there any free solutions to bypass IPTV blocking?
Free solutions for bypassing IPTV blocking exist but typically involve trade-offs in terms of performance, reliability, security, or ease of use compared to premium alternatives, though some free options can provide effective blocking countermeasures for users with limited budgets.
Free VPN services like ProtonVPN Free, Windscribe Free, and TunnelBear Free offer limited but functional VPN access that can bypass basic ISP blocking measures. However, free VPN services typically impose data usage limits, speed restrictions, and server limitations that may not support consistent high-definition IPTV streaming. Privacy concerns with free VPN services include potential data logging and advertising-based revenue models that may compromise user anonymity.
Public DNS services like Google DNS, Cloudflare DNS, and Quad9 provide free alternatives to ISP-provided DNS servers that can bypass DNS-based blocking measures. These services are easy to configure and don’t impose usage limitations, though they’re only effective against ISPs that use DNS filtering rather than more sophisticated blocking methods.
Tor browser provides free anonymous internet access that can bypass ISP blocking, though its performance characteristics make it unsuitable for IPTV streaming due to high latency and limited bandwidth. Tor is better suited for accessing IPTV service websites and account management rather than actual streaming applications.
Open-source proxy solutions like Shadowsocks and V2Ray can provide effective blocking countermeasures when properly configured, though they require technical expertise to set up and maintain. Community-maintained proxy servers are sometimes available for free, though their reliability and security cannot be guaranteed.
Router firmware alternatives like DD-WRT and OpenWrt are free and can unlock advanced networking capabilities that help bypass ISP blocking, though they require compatible hardware and technical knowledge to implement safely.
How do I choose an ISP that doesn’t block IPTV?
Choosing an ISP that doesn’t block IPTV requires careful research into provider policies, network infrastructure, and customer experiences, as ISPs rarely advertise their traffic management practices or blocking policies in marketing materials.
Research methodology should include examining multiple information sources including official terms of service, customer reviews, community forums, and regulatory filings that may reveal ISP attitudes toward streaming services and traffic management. Net neutrality compliance records can provide insights into ISP practices, while customer complaint databases maintained by regulatory agencies often include information about blocking and throttling issues.
Fiber-optic providers generally offer the best experience for IPTV users due to their superior bandwidth capacity and more modern network infrastructure that can handle high-bandwidth streaming without implementing restrictive traffic management. Google Fiber, Verizon FiOS, and municipal fiber networks typically maintain more neutral policies toward streaming services.
Municipal and cooperative ISPs often provide excellent alternatives for IPTV users, as these community-owned networks typically prioritize public service over profit maximization. Electric cooperatives that offer internet service and municipal broadband networks generally implement fewer restrictions on streaming services and maintain more transparent policies.
Business internet plans from traditional ISPs sometimes include stronger service level agreements and fewer restrictions compared to residential services, though they typically cost more. Small business plans may provide better protection against traffic management practices that affect IPTV streaming.
Contract negotiation strategies can help users secure better terms and protections against future policy changes. Users should specifically ask about traffic management policies, data usage limitations, and streaming service restrictions before signing service agreements. Month-to-month contracts provide more flexibility than long-term agreements if blocking issues develop.
Conclusion: Taking Control of Your IPTV Experience
Key Takeaways for IPTV Users
Taking control of your IPTV experience in an environment where internet provider IPTV blocking is increasingly common requires a comprehensive understanding of the technical, legal, and practical aspects of streaming content over internet connections. The strategies and solutions outlined in this guide provide IPTV users with the knowledge and tools necessary to maintain reliable access to their preferred content while navigating the complex landscape of ISP restrictions and blocking measures.
Understanding ISP motivations for implementing IPTV blocking helps users develop more effective countermeasures and set realistic expectations for long-term solutions. ISPs block IPTV services for a combination of technical, legal, and business reasons including bandwidth management, copyright protection, and competitive considerations. Recognizing these underlying motivations allows users to select countermeasures that address specific blocking methods rather than implementing generic solutions that may not be effective against their particular ISP’s restrictions.
Systematic detection and diagnosis of ISP blocking provides the foundation for implementing appropriate countermeasures. Users who can accurately identify whether they’re experiencing DNS filtering, port blocking, traffic throttling, or complete service blocking can select targeted solutions that address their specific situation. Comparative testing using VPN connections, alternative DNS servers, and different devices helps isolate ISP-specific issues from general connectivity problems or service outages.
Multi-layered protection strategies offer the most reliable approach to maintaining IPTV access in the face of evolving ISP blocking measures. Combining VPN services with DNS configuration changes, router-level optimizations, and alternative connectivity options provides redundancy that ensures continued access even when individual countermeasures become less effective. Defense in depth approaches also provide better protection against future blocking technologies that ISPs may implement.
Legal and ethical considerations should guide user decisions about which IPTV services to access and which countermeasures to implement. Focusing on legitimate IPTV services with proper licensing agreements eliminates legal risks while still providing comprehensive entertainment options. Privacy protection through VPN services and secure DNS configurations helps maintain user anonymity without necessarily facilitating access to unauthorized content.



2 Responses